Vector Addition: Geometric Method
+x is to the right; +y is up
Vector A has a length of 3.76 cm and is at an angle of 34.5 degrees above the positive x-direction. Vector B has a length of 4.53 cm and is at an angle of 34.1 degrees above the negative x-direction.
What is the sum (resultant) of the two vectors?
Here are three geometric methods to find the resultant:
Method 1
- Move the tail of A to the origin
- Move the tail of B to the tip of A
- The resultant goes from the tail of A to the tip of B
Method 2
- Reverse the roles of A and B in Method 1.
Method 3
- Move the tail of both vectors to the origin
- Complete the parallelogram
- The resultant goes from the origin to the opposite vertex of the parallelogram
To solve for the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector, apply the Cosine Law and the Sine Law to the triangle you obtain using one of the above methods.
Sine Law and Cosine Law
Although we often deal with right-angled triangles, many triangles do not have a right angle. The Sine Law and Cosine Law are often useful for those triangles.
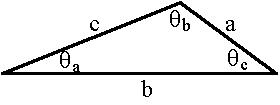
The Sine Law:
| sin(θa)
|  |
| a
|
|
= |
| sin(θb)
|  |
| b
|
|
= |
| sin(θc)
|  |
| c
|
|
The Cosine Law:
c2 = a2 + b2 - 2ab cos(θc)