P3)How much kinetic energy will an electron gain (in joules and eV) if it falls through a potential difference of 21,000 V in a TV picture tube?
SOLUTION:
The difference in potential (V) is 21,000 V.
The kinetic energy gained is 21 keV = 21,000 x
(1.6 x 10-19 J) = 3.36 x 10-15J.
P5)How strong is the electric field between two parallel plates 5.2 mm apart if the potential difference between them is 220V?
SOLUTION:
For a constant electric field (E) where the
displacement (d) is parallel to the field, V = E x d.
E = V / d = 220V / 0.0052m = 4.2 x 104 V/m
P12)An alpha particle (which is a helium nucleus, Q = +2e, m = 6.64 x 10 -27kg) is emitted in a radioactive decay with KE = 5.53 Mev. What is its speed?
SOLUTION:
KE = 5.53 Mev = 1/2 mv2
v = (2 KE / m)1/2 = [2 (
5.53 x 6) (1.6 x 10-19) / ( 6.64 x 10
-27)]1/2 m/s
v = 1.63 x 10 7 m/s
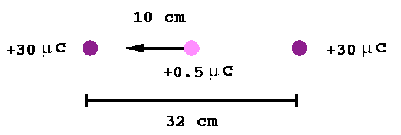
P15)A +30 µC charge is placed 32 cm from an identical +30 µC charge. How much work would be required to move a +0.50 µC test charge from a point midway between them to a point 10cm closer to either of the charges?
SOLUTION:

P33)How much charge flows from a 12.0-V battery when it is connected to a 9.00-µF capacitor?
SOLUTION:
C = Q / V
Q = CV = (9 x 10 -6F) (12V) = 108 µC
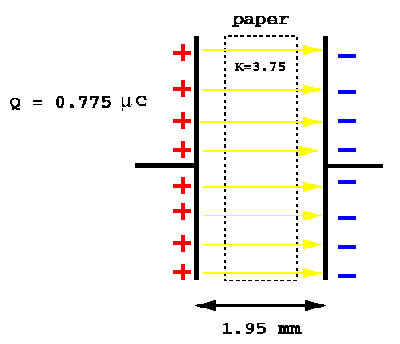
P40)The electric field between the plates of a paper seperated (K = 3.75) capacitor is 9.21 x 10 4 V/m. The plates are 1.95 mm apart and the charge on each plate is 0.775 µC. Determine the capacitance of the capacitor and the area of each plate.
SOLUTION:
P7)A 9.0-V battery is connected to a bulb whose resistance is 1.6 ohms. How many electrons leave the battery per minute?
SOLUTION:
V = I R (potential = current x resistance)
Q = I t (charge = current x time)
Ne = Q / e = I t / e
= (V / n) (t / e)
Ne = (9.0 V)(60 s) / [(1.6 ohms) (1.6 x
10-19C)] = 2.1 x 1021 electrons per minute
P12)What is the diameter of a 1.00-m length of Tungsten wire whose resistance is 0.22 ohms?
SOLUTION: