Lecture
11: Grand Unification of all Particles and Forces
1. Before class experiment #1: Cloud chamber reveals
tracks of charged particles
2. Before class experiment #2: Muon cosmic ray telescope
...half life of muon at rest = 2 micro sec even at speed
of light. At 1 nanosec/foot, muon only goes 2000 feet
how does muon get here from top of atmosphere? 7 miles
up (time dilation...see next lecture)
every second a cosmic ray muon pierces you...
3. Weak (Radioactive) Interaction: Power and Longevity
of the Sun
if 6 kinds of quarks and 6 types of leptons, why only
see up and down quark and electron?
weak interactions cause massive quarks and leptons to
decay into lighter quarks and leptons
weak interactions cause quark or lepton to transform
via W and Z force carrying particles
Why is sun 4.5 billion years old? slowness of weak interaction
Where does it get its power? nuclear fusion converting
mass to energy... ultimate source of all our energy
pp -> (pn) e+ v= d e+ v
d= deuteron = 2H11 = n+p
4. Radioactive Beta Decay of the Neutron ... Classic
Weak Interaction
neutron (udd) decays to a proton (uud) + electron + e-antineutrino
decay electrons initially called "beta rays" / didn't
know they were electrons
intermediate stages occur in <10-27 , second
not observable
5.Particle Decay Mediators
nucleus can decay into less massive nucleus by splitting
apart
how can a fundamental particle decay into another fundamental
particle?
a particle can decay into less massive particle + force-carrier
( W or a gluon) boson
boson then decays into other particles / mediating particle
decays / seems to violate conservation of energy because their high mass,
but "virtual" bosons exist so briefly no "rule" broken
6. Uncertainty and Virtual Particles
1927- Heisenberg's formulation of a fundamental property
of quantum mechanics:
it is impossible to measure both a particle's position
and its momentum exactly
the more precisely we determine one, the less we know
about the other 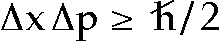 ,
and
,
and 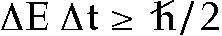
7. Neutrinos
have no charge, and little, if any, mass / almost never
interact with other particles / pass right through earth without interacting
/ 1/sec pass through you...and only one will interact in your lifetime
/ produced only in weak interaction decays
observation of radioactive decay of neutron reveals the
neutrino's existence.
sum of momenta of electron and proton not equal to the
original momentum of the neutron
some other particle accounts for the missing momentum:
the neutrino
neutrinos: produced by weak interactions in stars and
supernova, 99% of energy a lot of them in the Universe like 3 degree big
bang photons
8. Antimatter
every particle (matter) has corresponding antiparticle
(antimatter), the electron (e-) antiparticle is a positron (e+)
antiparticles are same as corresponding matter particle,
except all charges opposite e.g. proton is electrically positive; anti-proton
is electrically negative, but both have exactly same mass and affected
in the same way by gravity
when particle and its antiparticle meet, annihilate into
pure energy which this energy may materialize into any particle/anti-particle
pair, or into neutral force-carrier particles, such as photons, Z bosons,
or gluons
9. Anti-proton Annihilations in Hydrogen
photograph of antiproton colliding with a proton in liquid
hydrogen / eight pions produced / one pion decays into muon and neutrino
positive and negative particles curve in opposite directions in magnetic
field
bubble chamber more advanced detector than cloud chamber,
but much less powerful than modern detectors ...see cloud chamber in class
experiment
10. Discovery of Top ...March 1995...one of first
events:
top quark --> bottom quark + W+ --> e+
+ neutrino / bottom quark emerges as neutral anti-B meson and decays into
Jet 4
antitop quark --> antibottom quark + W- -->
anti-up quark + down quark/antibottom quark (Bo
meson) decays into Jet 1
cannot tell which of Jets 2 and 3 is the anti-up quark
and which is the down quark
bottom & antibottom meson have long lifetimes and
enough energy to travel visible distance before decay / both emerge as
neutral particles, neither leave tracks until they decay
neutrino leaves no track, presence is inferred by missing
momentum and energy
11. Annihilation of Antimatter Positron Electron Tomography
Example: e+ + e- -->  +
+  (photon
+ photon) / Experiment: 22Na nucleus (in salt) is unstable,
emitting positron / positron finds an electron in NaCl / crystal annihilation
produces 2 back-to-back gamma rays
(photon
+ photon) / Experiment: 22Na nucleus (in salt) is unstable,
emitting positron / positron finds an electron in NaCl / crystal annihilation
produces 2 back-to-back gamma rays
12. Positron Emission Tomography
Application: ingested radioactive salt is rapidly
metabolized, concentrated by cancer / trace back 2 gamma rays to source
with < 1mm accuracy, before tumor metastasizes
physicists can also annihilate two particles of tremendous
energies to create new, massive particles
13. Electromagnetism ... the second step on the road
to unification
first: Newton unified planetary & terrestrial gravity
Maxwell: second unification of forces - electricity and
magnetism / electrical charge (positive/negative) and magnetism (north/south)
are different aspects of the same force
photons absorbed or radiated by any accelerating electrically
charged particle
photons have zero mass / always have the speed c = 300,
000, 000 m/s in a vacuum ...in any frame of reference!!!
...and they behave as particles...see in-class experiment
14. Photons as Particles... in-class experiment
absorb light and see decrease of signal in detector /
number of photons decreasing, not energy of each, until reach a minimum
size pulse...cannot get 1/2 / photon more attenuation, fewer photons, but
all of same energy
15. Unified Electroweak Interaction
weak charges closely related to electromagnetic charges
/ force not actually small at very short distances, where weak interaction
comparable to electromagnetic.
difference in strength due to huge difference in mass
between W and Z, (very heavy) and massless photon
Next unifications in progress 1) electroweak with strong
(Grand Unified Theory (GUT)) 2) electroweak/strong with gravity (string
theory) ...again, another Nobel prize for your generation
16. Grand Unification Theory
theory which (we hope!) unifies the strong, weak, &
electromagnetic interactions, more data is needed to tell which of many
theories describes nature
all interactions we observe appear to be different aspects
of the same, unified interaction / current data and theory show that all
forces merge into one force at a high enough energy, at small distances,
and at early times in the universe
this primordial force-carrier particles would cause the
proton to decay / such decays extremely rare; otherwise our world would
not exist today/ and asymmetric, otherwise universe would not be dominated
by matter, rather than antimatter.
17. Summary: A Short History of the Universe
The active forces and particle in each era: big bang,
age of leptons, age of nucleons, age of ions, age of atoms, and age of
stars